Modern business operations now depend on digital commerce to offer online platforms for product and service sales. Modern criminals are attacking e-commerce platforms with growing frequency. E-Commerce Security: Security protection is the most pressing need at this time. Security creates a defensive barrier to protect customer data during electronic purchases, including e-commerce encryption, which ensures that sensitive information is securely transmitted. This paper examines how security functions, including encryption, protect businesses from internet dangers using operational safety measures.
What Is E-commerce Security?
Online transactions and company information remain protected through E-commerce safeguards that block dangerous digital threats. It protects both your business operations and user data, such as e-commerce payment gateways while offering defence security, e-commerce encryption, and easy user access mechanisms.
Key Objectives of E-commerce Security:
- Confidentiality: Our system blocks unauthorized individuals from accessing and working with secret data.
- Integrity: Our protection routines block all attempts from users who try to alter or erase their information without permission.
- Authentication: Our system must authenticate users to protect against online financial fraud.
- Non-repudiation: Make sure every part of an e-commerce transaction accepts its role in the process.
- Availability: We need to keep our e-commerce platform running 24/7.
Importance of Maintaining E-commerce Security
- Protecting Customer Trust: System data break-ins allow fraudulent individuals to steal customers’ personal information and financial details.
- Preventing Financial Losses: Cyber attacks include credit card fraud and ransomware, through which businesses lose considerable sums of money.
- Securing Business Data: An e-commerce platform holds significant customer information that becomes a threat when enemies gain access and use the information after a breach.
- Regulatory Compliance: We must implement the GDPR and PCI-DSS standards for legal safety measures.
- Advanced Threats: Modern cyber threats make us continuously protect and update our security tools.
- Business Continuity: The right security measures let your business work without technical interruptions.
Key Features of E-commerce Security Threats
- Automated Attacks: Through an automated robot program, threats penetrate system vulnerabilities.
- Data Breaches: Digital intruders specifically target secret information belonging to customers and businesses.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Attackers use false methods to target vulnerable people.
- DDoS Attacks: Threats send excessive website traffic to break down web services.
- Financial Fraud: Hackers scam money through false transactions, and buyers file chargeback requests while doing payment fraud.
E-Commerce Security: Key Threats
1. Phishing Attacks

Internet criminals disguise themselves as trustworthy sources to trick users into handing over their login passwords and credit card numbers. Attackers create phony email websites and message copies of reliable brands to fool users into typing their personal account information. Companies suffer from financial and public image problems and client information exposure when cyberattacks occur. E-commerce platforms face high risk because they handle large numbers of customers and money transactions. E-commerce encryption plays a key role in protecting sensitive data, while e-commerce cybersecurity tips help businesses fortify their defenses against these types of threats. Additionally, adopting MTA STS can significantly improve email security by preventing man-in-the-middle attacks and ensuring that emails are only sent over secure connections.
How to prevent it:
- Implement email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC).
- Educate employees and customers on phishing tactics.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Regularly update and monitor email security filters.
2. Malware Attacks

Computer threats like viruses and ransomware are part of malware that target and destroy electronic systems. Malware intruders in e-commerce set up attacks to take customer information with failed website performance and ransom requirements. Cybercriminals spread malware by sending risky attachments and fake websites that cause big financial problems and can get them in legal trouble.
Some even use phone calls to get into the internal networks of e-commerce businesses, making it essential for them to use a phone carrier lookup tool to identify the origin of suspicious calls and take appropriate security measures to protect their sensitive data and networks. To combat these threats, e-commerce cybersecurity tips are essential for businesses to protect their platforms, while e-commerce encryption ensures that sensitive customer data remains secure during online transactions.
How to prevent it:
- Regularly update antivirus software and firewalls.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Monitor systems for unauthorized activities and anomalies.
- Educate employees on safe browsing and email practices.
3. SQL Injection
A cyber attacker performs SQL injection by inserting dangerous SQL commands into web applications to change the data stored in the database. The attacker uses this breach to reach private data sources, including customer records and their payment and login access. E-commerce security platforms risking their customer data face serious compliance challenges when they don’t validate user inputs correctly,y which lets attackers launch SQL injection attacks.
How to prevent it:
- Use parameterized queries and prepared statements.
- Conduct regular penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
- Deploy web application firewalls (WAFs) to detect and block malicious queries.
- Restrict database access based on user roles.
4. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
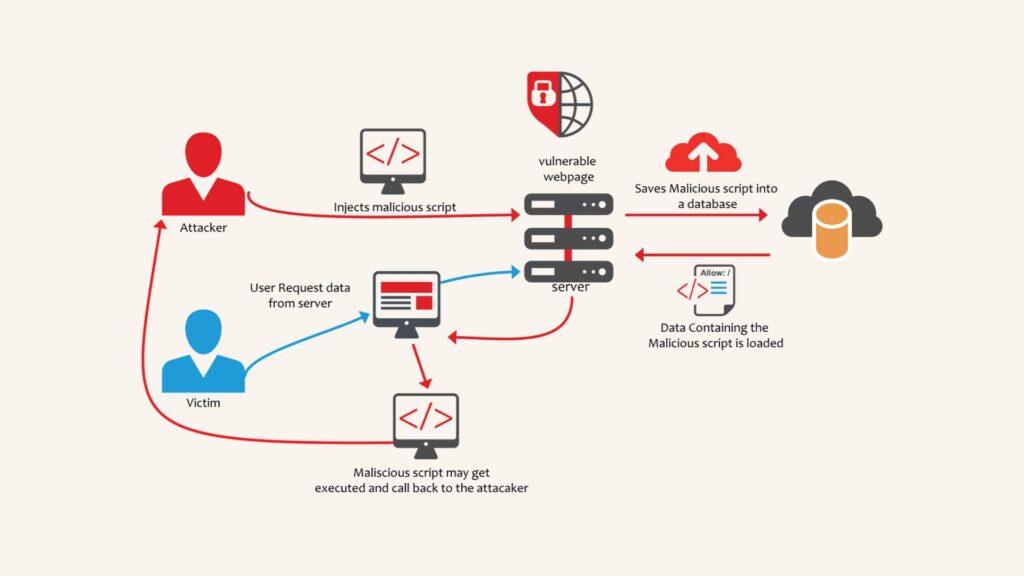
XSS attacks inject harmful scripts into web pages for other users to see while they browse. Attackers use the scripts to hijack web users’ protected information by taking their cookies and tokens and then pushing them to illegal websites. The attackers weaponize weak spots in user entry fields especially search and comment sections to implement their scripting attacks.
How to prevent it:
- Validate and sanitize all user inputs to prevent script injection.
- Implement a Content Security Policy (CSP) to control resource loading.
- Use security frameworks that automatically escape output data.
- Regularly scan web applications for vulnerabilities.
5. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
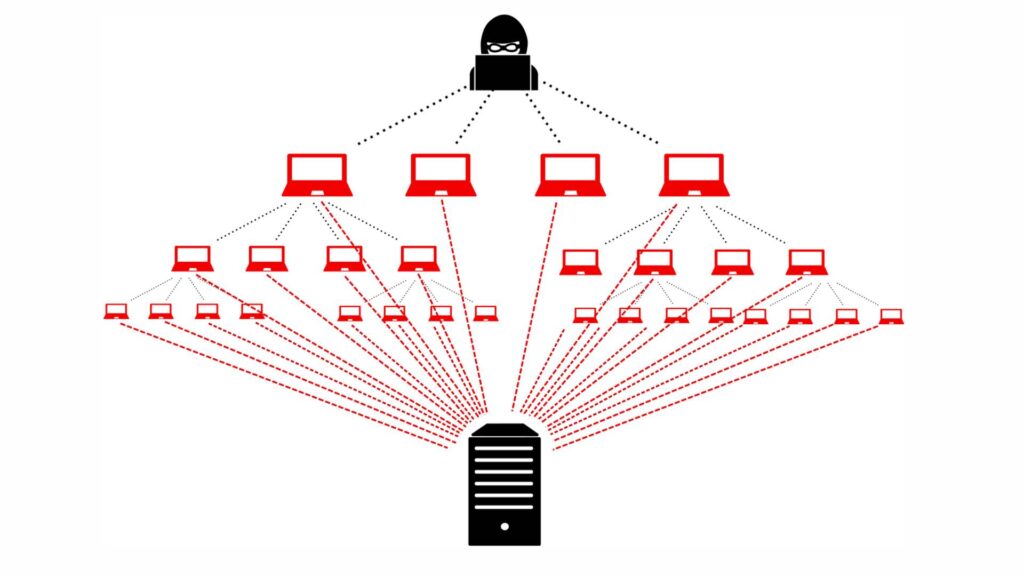
Through DDoS attacks, hackers generate so much online traffic that genuine shoppers become denied access to e-commerce security sites. Cyber attacks keep websites down for long periods, hurting businesses and their users financially. Cybercriminals spread computer attacks from numerous hacked devices to strike online systems through their distributed network. So, make sure to train your employees on cybersecurity practices and leverage reliable IT procurement services to minimize vulnerabilities, detect threats early, and ensure your business has the necessary security infrastructure to defend against potential cyberattacks.
How to prevent it:
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute traffic loads.
- Employ DDoS protection services to detect and mitigate attacks.
- Monitor traffic patterns to identify unusual spikes.
- Develop a response plan to handle potential attacks.
6. Carding Attacks

Online thieves test stolen credit card information on small purchases to verify if it is genuine at retail websites. A fraudster uses small transactions to check stolen card information on websites before conducting costly illegal activities. These digital attacks result in both financial losses from chargebacks and destroy a business’s public image. To mitigate such risks, e-commerce encryption ensures secure transactions and an e-commerce security audit can help identify vulnerabilities in a business’s online platforms.
How to prevent it:
- Implement CAPTCHA verification to prevent automated attacks.
- Use fraud detection tools that analyze transaction patterns.
- Monitor transactions in real time to detect suspicious activity.
- Block high-risk IP addresses and regions.
7. Ransomware Attacks
Malware called ransomware blocks access to files by encryption and forces the victim to pay before they can recover their data. Cybercriminals seek out e-commerce businesses because they process essential operational data and necessary customer transactions. Ransomware threats seriously affect business operations and hurt company revenues while eroding customer faith in the business.
How to prevent it:
- Maintain regular backups and store them securely.
- Train employees to recognize phishing attempts.
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.
- Limit access to critical data and applications.
8. Insider Threats
Staff members including contractors and business associates abuse their permission levels to take or harm sensitive data. These threats result in data breaches while stealing company information and stopping business operations. Employees who are angry or driven by money motives usually launch these attacks.
How to prevent it:
- Implement strict access control measures and role-based permissions. Compare Cloudflare vs Umbrella to determine the most effective solution.
- Monitor internal activities and log user access.
- Conduct background checks and employee training.
- Encourage a culture of security awareness.
9. Brute Force Attacks
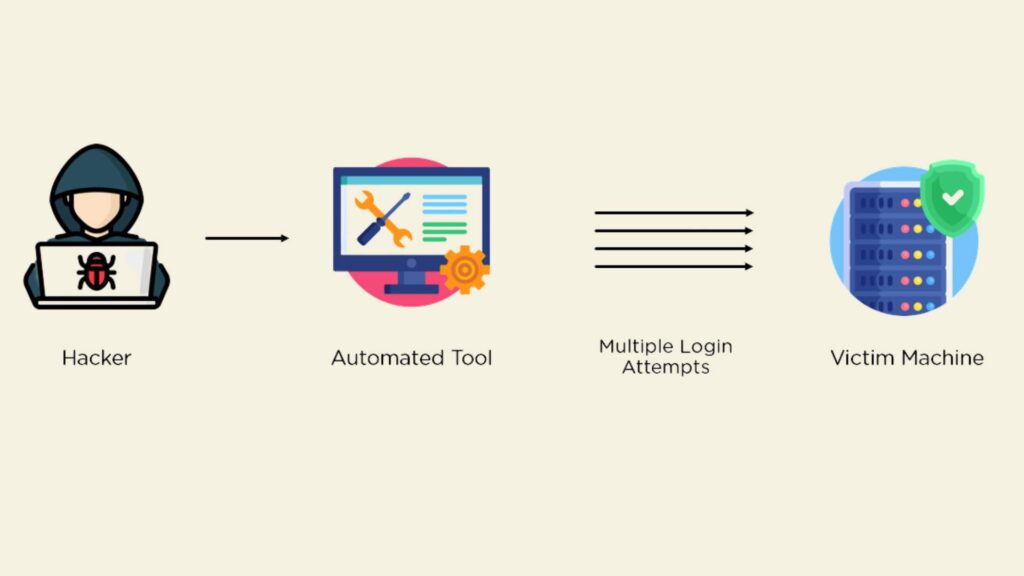
Having automated bots attempt multiple password combinations to enter e-commerce systems without permission is what brute force attacks mean. Most automated bot programs focus on cracking easy or standard user credentials. To protect against these attacks, data protection e-commerce strategies are vital, and an e-commerce security audit can help identify and address vulnerabilities in the system to prevent unauthorized access. AI-driven cybersecurity can strengthen defenses by detecting threats in real-time. Deploying a local LLM helps analyze security logs and identify vulnerabilities while keeping sensitive data on-premises.
How to prevent it:
- Enforce strong password policies with complexity requirements.
- Implement account lockout mechanisms after multiple failed attempts.
- Use CAPTCHA to prevent automated login attempts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
10. Supply Chain Attacks
Cybercriminals break into a company through unauthorized access to its external vendors and suppliers. Cyber crooks use their access to software companies and supply chain partners to take over company systems and spread either computer threats or personal data.
How to prevent it:
- Conduct regular security audits of vendors and suppliers.
- Use only trusted and verified third-party services.
- Monitor supply chain partners for compliance with security standards.
- Implement data segmentation to limit exposure in case of a breach.
Best Practices for E-commerce Security
Since businesses are more focused on their sensitive customer data, security is very important. Robust security measures can be implemented to prevent cyber threats, earn customer trust, and maintain regulatory compliance. Here are the ten best practices for improving e-commerce security:
1. Use HTTPS for Secure Connections
Data sent from a user’s browser to your website will be encrypted with HTTPS. By doing so, you safeguard sensitive information like payment details and login credentials from intercepting malicious users. Having an SSL/TLS certificate means securing your data and your customers’ trust or confidence.
2. Implement Strong Password Policies
Weak passwords are one of the common ways. Use correct password policies while creating passwords which should include uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Do suggest that his passwords be changed regularly the site maintains to have account lockout mechanisms which if a bad guy tries to access the user account ukg pro should be locked out.
3. Regularly Update Software and Plugins
Old software, plugins, and extensions may have vulnerabilities that a hacker can exploit. It is important to keep your applications and libraries up to date because regular updates help to ensure that security patches and bug fixes are applied thus reducing the risk of cyber attacks. Go ahead and update whenever you can — be safe. If your business relies on third-party integrations, ensure that your vendor portal is also regularly updated to prevent unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
4. Conduct Frequent Security Audits
In e-commerce platforms, regular security audits help in identifying vulnerabilities and gaps. Perform penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks. A strong data security posture management ensures these measures are effective and proactive in mitigating risks.
5. Employ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is an additional authentication method that requires the user to log into a system (e.g. a password or a 1-time code sent to their phone) to access sensitive data. Nearshore software development can help you implement robust security measures, ensuring teams follow best practices for data protection. It is much more difficult for an unauthorized user to gain access to the data.
6. Use Reliable Payment Gateways
Opting for trusted payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or Square helps secure deals by following industry security standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). To mitigate risks, do not store sensitive payment information on your servers.
Conclusion
Ensuring “E-Commerce Security: Key Threats and Best Practices” protects sensitive customer and business information. With this, e-commerce businesses can learn to understand the key threats and implement best practices to build trust, meet compliance, and grow sustainably.
FAQs
1. What is the number one e-commerce security threat?
The major threats to e-commerce security are phishing attacks, data breaches, credit card fraud, malware, and account takeover.
2. How does HTTPS help in e-commerce security?
HTTPS encrypts a user’s data between the user and the website making it so that sensitive information such as a payment will be safe and making it trustworthy for the customer.
3. If your e-commerce site gets hacked, what should you do?
Shut the site down, send your hosting provider, remove the malware, change passwords, notify customers if so, and run a security audit with a relaunch.
4. When should you perform security audits?
A minimum quarterly would be a minimum, though high transaction businesses would need to be more frequent to find vulnerabilities and stay compliant.
5. What are the critical e-commerce security regulations?
Compliance with these strict legal standards, including PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA, and so on is ensured through the secure handling of the customer data.

